What is cyber extortion, how to protect yourself, and what to do if you are a victim. What are the costs and the risks for companies.
Index
- What is cyber extortion?
- Types of cyber extortion
- How does cyber extortion work?
- What laws apply in case of cyber extortion?
- How to report a case of cyber extortion?
- What to do if someone threatens you online?
- The cost of cyber extortion
- Examples of cyber extortion
- How does cyber extortion affect reputation?
- Conclusions
- FAQ
Do you want to delete personal and private information from the web?
ReputationUP guarantees the elimination of any personal and private information from any Web platform
What is cyber extortion?
Dealing with cybersecurity plays an essential role in managing your online reputation.
An attack on your digital identity or any cyber attack can negatively affect your brand reputation from an image point of view and an economic point of view.
A particular type of cyber attack is cyber extortion.
This extortion is perpetuated online by forcing an individual or a company to pay a ransom in exchange for recovering access to stolen IT resources.
According to the definition that we find in the report published by IC3, the word extortion is explained as:
“Unlawful extraction of money or property through intimidation or undue exercise of authority. It may include threats of physical harm, criminal prosecution, or public exposure”.
In the same document promulgated by the organization that deals with cyber security of the US government is possible to read interesting data on cyber extortion.

There were 39,360 cases of online extortion in 2021, down from the previous three years.
The peak of cases was recorded in 2020, with approximately double: 76,741 complaints.
Types of cyber extortion
Cyber extortions have a particular purpose: to block or limit the functions of a device until a ransom is paid.
The assets blocked by a cyber attack aimed at digital extortion can be of any nature.
This can be, for example, sensitive information of the employees of a company or its customers; confidential data which, if disclosed, could damage the online reputation.
Likewise, there are different types of cyber extortion, which spread through means and attacks of varying severity.
The most common are certainly ransomware and DDoS attacks.
Other ways of spreading include:
- Online smear campaigns;
- Spam;
- False-negative reviews;
- Phishing.
They all act on the theft of information intending to damage the online reputation.
Sextortion represents a particular case of cyber extortion.
This crime is defined by the Cambridge Dictionary as follows:
“The practice of forcing someone to do something, particularly to perform sexual acts, by threatening to publish naked pictures of them or sexual information about them.”
It is, therefore, a sexual threat.
Ransomware
The term ransomware defines malware used by hackers to infect victims’ devices, blocking their functionality.
By exploiting the users’ vulnerabilities and ingenuity, the attack infiltrates the system by encrypting files and information.
The most used infiltration techniques exploit phishing emails, unsecured web networks, or cybersquatting, which involves forging websites.
Hackers make sure that the victim is directly responsible for the attack.
These social engineering tricks push users to download the malware directly to the device.
From then on, the malicious software will block access to files and systems to which access can only be regained following the payment of the ransom.
A screen that warns of the infection will appear, and the user will have a limited time to pay.
Lately, a type of ransomware attack called double extortion is spreading, which, in addition to encrypting the data, creates a backup copy of the files to lay them on the web even after the ransom has been paid.
DDoS attacks
Another type of cyber extortion attack is DDoS (Distributed Denial-of-Service), which means an interruption in the distribution of the service.
This type of attack is carried out as a joint action by several servers that disrupt a website.
The criminals send such a large amount of data that the server crashes, sending it into a tailspin.
DDoS attackers use a mixed attack strategy that combines various attack methods with social engineering, credential theft, and physical attacks.
According to Kaspersky, there were 91,052 DDoS attacks in the first quarter of 2022, four times the same period of 2021.

This type of attack aims to render the network temporarily unusable.
The damage of this type of attack is evident if we consider the example of an eCommerce platform.
Even if it is only a temporary block, which generally does not exceed a few hours, DDoS attacks cause significant economic losses.
How does cyber extortion work?
Cyber extortion works differently depending on which attack technique is chosen.
However, all are intended to limit the hardware or software functionality of the attacked infrastructure.
The procedure, therefore, consists of a series of recurring phases:
- The hacker sends the victim a virus that infiltrates the device.
Criminals usually mask malware within phishing emails or through other social engineering systems.
- The virus spreads by encrypting all files.
Once the victim has downloaded the malware, it scans all files on the device and makes them inaccessible with an encryption system.
- The hacker demands the payment of a ransom to restore the data.
To restore access to the system, you must pay the ransom to receive the decryption key.
In this way, extortion takes place.
This type of attack requires joint action for its resolution.
On the one hand, to block the action of hackers and recover encrypted files; on the other hand, to eliminate information disseminated online and restore reputation.
ReputationUP and HelpRansomware offer services to guarantee you complete protection of your digital identity.
Need help protecting your reputation?
Remove all negative content against your brand and publish positive content that re-launches your digital image
How many cybercriminals are there?
Establishing a precise number of hackers responsible for various cybercrimes is certainly not easy.
Cyber-attacks have increased dramatically in recent years, and the number of cybercriminals goes hand in hand.
The predictions for the future are no better.
Indeed, the development of many IT-disliked SMEs could give rise to an ever-increasing number of attacks.
However, it is possible to draw up a list of the different types of hackers:
- Financially motivated cyber criminals;
- Ethical hacking managers;
- Government-supported cyber criminals;
- Script kiddies, also known as green hat hackers, looking only for fame;
- Cyber terrorists.
Added to these are internal hackers, such as employees who steal information from the companies they work for.
What laws apply in case of cyber extortion?
At a legal level, the United States Code includes in article 873 the crime of extortion and its penalty:
“Whoever, under a threat of informing, or as a consideration for not informing, against any violation of any law of the United States, demands or receives any money or other valuable thing, shall be fined under this title or imprisoned not more than one year, or both”.
For its part, in the United Kingdom, Theft Act 1968 indicates the following:
- A person is guilty of blackmail if, with a view to gain for himself or another or with intent to cause loss to another, he makes any unwarranted demand with menaces; and for this purpose a demand with menaces is unwarranted unless the person making it does so in the belief:
- That he has reasonable grounds for making the demand; and;
- That the use of the menaces is a proper means of reinforcing the demand.
- The nature of the act or omission demanded is immaterial, and it is also immaterial whether the menaces relate to action to be taken by the person making the demand.
- A person guilty of blackmail shall on conviction on indictment be liable to imprisonment for a term not exceeding fourteen years.
In Europe, citizens can benefit from the GDPR when their data or information is exposed to the media.
In this sense, you can request the Right to be Forgotten to remove defamatory content from a search engine.
Do you want to exercise your right to be forgotten?
ReputationUP eliminates any obsolete content (links, photos, videos, comments, content, reviews) and guarantees your right to be forgotten and digital privacy
Is cyber extortion a crime?
As can be easily deduced from the articles listed above, the law has emphasized cyber attacks aimed at extortion.
This condition highlights how cyber extortion is, in effect, a crime.
However, the punishment of the crime depends on the possibility of being able to identify the person responsible for the attack.
Each country has different rules and provisions; the penalties vary according to the severity of the attack and the number of threats created within a corporate or private system.
Indeed the activity of a hacker is not legal.
Still, it must not be confused with the activity of IT technicians who can attack a computer system to evaluate its penetrability.
In the latter case, there is no offense, and no crime is involved.
What is the FBI’s position on cyber extortion?
The FBI has a section entirely dedicated to investigating computer crimes.
Its page says that it investigates cyber crimes involving criminal acts and national security issues.
Examples of criminal acts would be using a computer to commit fraud or the Internet to transmit obscene material.
However, in national security, the FBI investigates criminal matters involving the nation’s computerized banking and financial systems, the various emergency networks, and telecommunication systems.
How to report a case of cyber extortion?
To report a case of cyber extortion in the UK, you must contact the National Fraud and Cyber Crime Reporting Center on its website.
Login into your account and fill in the forms following all the steps and provide the requested information.
Before forwarding the discussion on the methods to be applied to the report, it is appropriate to underline which attacks can be reported.
The cybercrimes that can be reported are:
- Theft of a vehicle;
- Suspicious online behaviour with or towards a child;
- Online hate or bullying crime, material or messages;
- Counterfeit medicine or medical devices available to purchase online;
- Business or personal tax fraud or a related HMRC (Her Majesty’s Revenue and Customs) matter;
- Benefit fraud;
- Immigration fraud;
- Counterfeit Currency.
As far as cyber extortion is concerned, we advise you, if possible, to go to a Police office to better explain all the details of the affair.
For the USA, you can report the crime filling in the form on the IC3 website.
What to do if someone threatens you online?
When a hacker threatens you online after a cyber attack, keep calm.
Even if it is difficult, considering your situation, try to stay clear-headed:
- Never pay the ransom.
It may seem like the most straightforward and fastest solution to fix everything, but it is not the case: if you pay the ransom, hackers will consider you as an easy target and will target you multiple times;
- The first thing to do is report the cyber extortion to the competent authorities.
Screen conversations, whether via email or otherwise, as evidence of the crime;
- Contact an expert company.
If you see compromising material appearing online, contact ReputationUP.
The company has over twenty-five years of experience managing online reputation and eliminating defamatory content.
Need help protecting your online privacy?
ReputationUP guarantees the elimination of any private and personal information (name, number, address, photo, video) from any Internet platform
Can I report someone for cyber extortion?
As already highlighted in the previous lines, the British and American laws consider the cyber extortion attack illegal.
You can report this event anytime, especially if you feel threatened or in danger.
This condition also extends to company assets and the impossibility of using the work systems.
If your data has been published online, in addition to the complaint, you can contact a company of experts in deleting URLs from Google such as ReputationUP.
Do victims have to pay the ransom for cyber extortion?
One thing is clear: you must never pay the ransom, neither of cyber extortion nor any other online crime.
The official government position is summarized in the document signed by OFAC and FinCEN, two bodies headed by the US Treasury:
“Companies that facilitate ransomware payments to cyber actors on behalf of victims, including financial institutions, cyber insurance firms, and companies involved in digital forensics and incident response, not only encourage future ransomware payment demands but also may risk violating OFAC regulations.”
The reference to ransomware is also to be extended to other extortion crimes.
Not paying the ransom is essential because otherwise, further extortion is a risk over time.
Therefore, what seems to be the easiest solution turns into a conviction for the company.
HelpRansomware’s IT professionals will unlock your corporate or private system and allow you to return to normal work activities.
Also, ReputationUP remove data published by ransomware.
The cost of cyber extortion
To consider the overall cost of cyber extortion, we need to consider the cost of the ransom and other variables.
In addition to the potential cost of ransom, a cyber-attack also entails high costs in blocking work.
Therefore, the time lost in trying to solve the problem must also be included in the calculation.
Similarly, any information leakage must be considered as an additional cost.
According to the aforementioned IC3 report, considering the complaints of victims in the United States, the cost of cyber extortion amounts, in 2021, to 60,577,741 dollars.
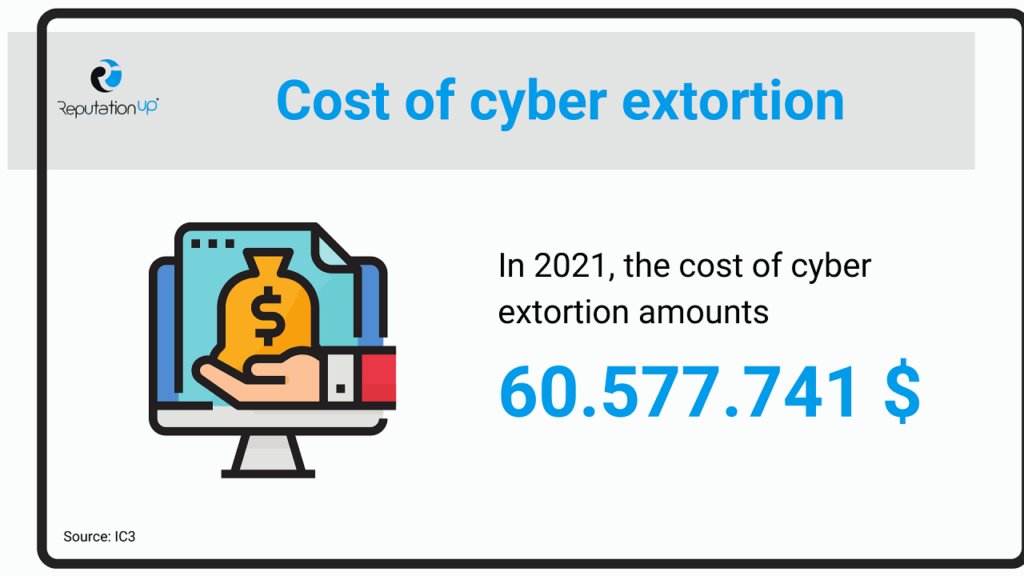
To these should also be added the costs of the ransomware ransom, which again only based on the complaints, is 49,207,908 dollars.
What are the risks of cyber extortion?
Being the victim of cyber extortion carries several risks.
Hackers can potentially block any file in your network infrastructure, from an employee/customer database to accessing a Word or Excel document.
However, three main risks can be identified: personal data, threats, and reputation:
- Personal data: blocking company personal data and those of your customers can expose your company and your catchment area to possible cyber-attacks;
- Threats: one of the most common risks lies in constantly being subjected to threats from cyber criminals;
- Reputation: Whenever your IT infrastructure system suffers an attack of this type, your company’s digital reputation drops dramatically.
When they have to deal with a blocked platform or service, customers are led to change their website.
Furthermore, any private and personal information disclosure can decrease customer confidence in your business.
Which companies can suffer from cyber extortion?
In an age where all companies have networked systems to work, potentially all are exposed to cyber extortion.
Hackers tend to target structures with less robust and efficient protection or those that handle data with specific characteristics.
For this reason, among the types of companies most affected are those small and medium-size.
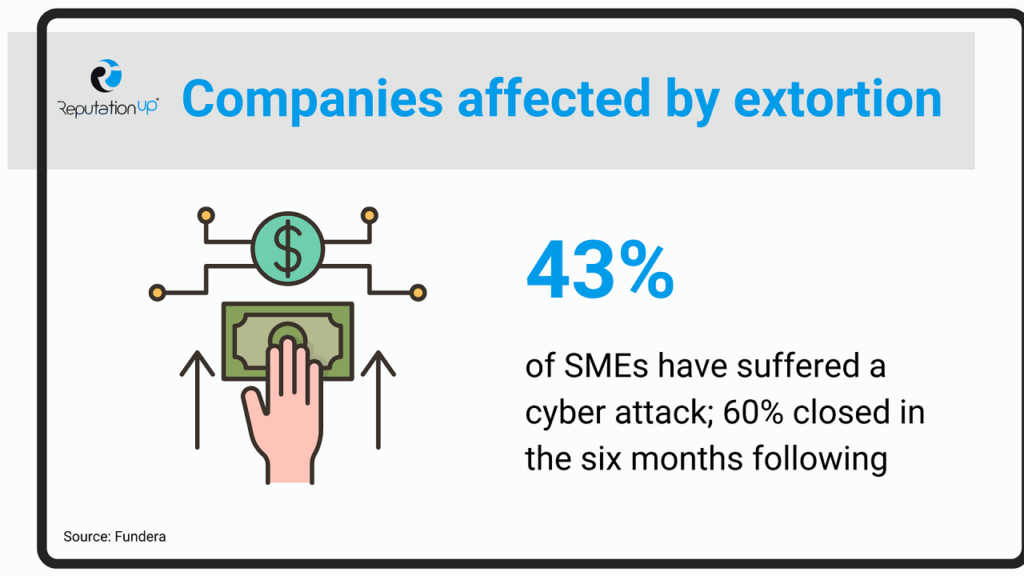
A study conducted by Fundera reports that 43% of SMEs have suffered a cyber attack; 60% closed their business in the six months following the attack.
The most affected sector, however, remains the healthcare sector.
In this case, we are dealing with infrastructures that cannot afford the interruption of services and therefore pay the ransom to try to solve the problem in the shortest possible time.
The ranking of the most affected companies is as follows:
- Technologies and communications: this sector has suffered a substantial increase following the metaverse‘s creation.
The development of a new socialization platform has increased the opportunities for online exchange and, consequently, also the opportunities to inflict extortion;
- Finance: this is another very profitable sector because it needs to protect the personal data of customers;
- Energy industry: this sector opens the doors of hacking to potential terrorist attacks;
- Construction: the attacks on this sector demonstrate the importance of the human factor, training, and digital education.
Apart from the eCommerce companies, caught by the DDoS attacks.
Again, blocking the online store with DDoS systems forces sellers to pay as quickly as possible.
Examples of cyber extortion
It is interesting to analyze some real examples to get a clearer idea of what a cyber extortion attack is and how it develops:
- Nokia
Back in 2007, hackers stole the source code of the operating system of the smartphones produced by the Finnish multinational.
The criminals threatened to reveal the key to the public, allowing other criminals to infect millions of smartphones and set off a chain reaction.
As revealed years later by the Finnish newspaper MTV, Nokia allegedly paid the ransom of millions of euros to protect its data;
- Domino’s
The famous fast-food chain was attacked by hacker group Rex Mundi in 2014.
The attack had stolen the data of 650,000 French and Belgian customer accounts, and the hackers demanded a ransom of 30,000 euros.
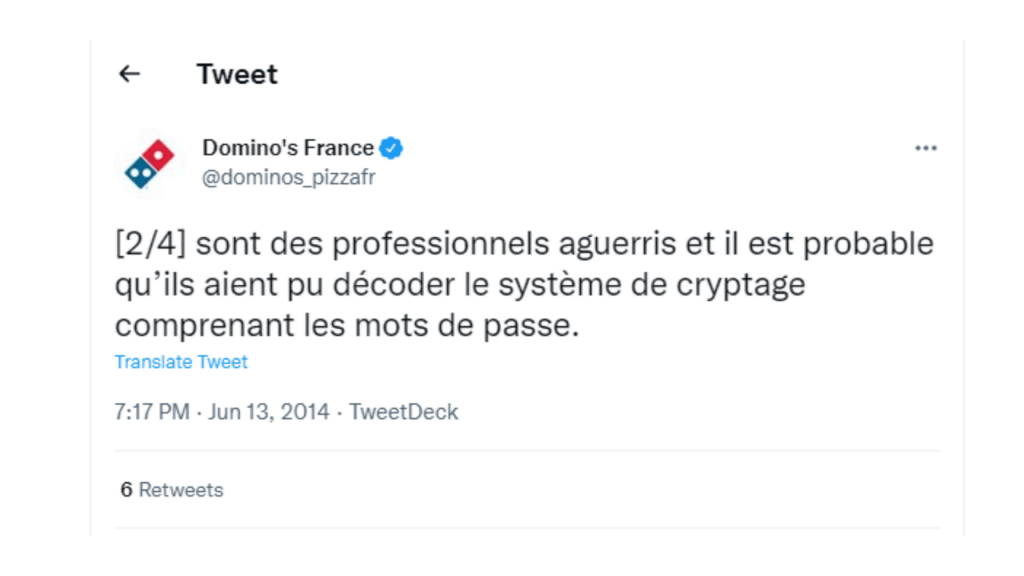
As announced on its Twitter profile, the company refused to pay the ransom and urged customers to change their login passwords, even if the stolen data contained no financial information;
- Code Spaces
This is one of the few cyber extortion cases that led to the closure of a company.
The hackers first attacked the code hosting company via DDoS, and then they took over the Amazon EC2 control panel.
It permanently deleted the storage volumes, backups, and system configurations.
The company refused to pay the ransom and tried to regain control of its facility, but without success.
How does cyber extortion affect reputation?
One of the most damaging aspects of cyber extortion is the negative impact on corporate reputation.
When personal and private information is released online, it can have repercussions.
On the other hand, at the corporate level, your image can be ruined by blocking your website, which would immediately divert your customers elsewhere.
Or your customers may perceive your computer system as unsafe.
In both cases, your company will face a reputational crisis before the economic loss.
This is why it is crucial to have a strategy for managing these problems.
As a company and as an individual, you should develop a reputational risk plan in which all the consequences of a cyber or media attack on your image are calculated.
The damage to reputation is amplified if the company has a lot of online resonance.
Do you want to protect your reputation from haters and fake news?
You risk losing 22% of your revenue if potential customers find a single negative link on Google’s first page
How to protect a company from cyber extortion
Companies can also refer to the ISO / IEC 27001 standard for official data protection guidelines.
In any case, to effectively manage its security, therefore, a company must take several steps:
- Top management must promote safety initiatives;
- Company personnel must be appropriately trained: most cyber attacks occur due to employee distraction;
- Dedicated software: a company must be able to count on a software sector capable of monitoring threats on corporate devices in real-time;
- Cloud and backup services: using hardware and software that saves data in the cloud allows you to have a copy of the data even after the attack, and therefore, you will not need to pay the ransom.
Companies must understand that protecting their IT systems is essential to avoid intrusions and thus preserve a good image online and offline.
Acting on IT protection means working on protecting company assets, both in strictly economic terms and in terms of information.
Conclusions
The risks associated with cyber extortion are significant for individuals, SMEs, and large companies.
Although some working sectors are less tied to this problem, it is essential to have adequate tools to avoid economic losses and brand reputation.
Here are the conclusions you can draw from this article:
- Cyber extortion is extortion that is perpetuated online by forcing an individual or a company to pay a ransom in exchange for recovering access to stolen computer resources;
- In 2021, there were 39,360 cases of online extortion;
- Cyber extortions have a particular purpose: to block or limit the functions of a device until a ransom is paid;
- The most common types of cyber extortion are ransomware and DDoS attacks;
- Considering the reports of the victims in the United States, the cost of cyber extortion amounts, in 2021, to 60,577,741 dollars;
- Cyber extortion negatively affects a company’s online image and its brand reputation.
Businesses and individuals alike need to have various means to protect their information from attacks.
If you have been the victim of cyber extortion, you can contact ReputationUP, a world leader in removing harmful content from the web and managing online reputation.
Do you want to remove negative images from the web?
ReputationUP guarantees the elimination of any negative image from any platform
FAQ
If you are a victim of sextortion or any other type of cyber extortion, the first thing to do is report everything to the police.
Don’t give in to blackmail; you never have to pay the criminals, but you have to act quickly.
If they have published private photos or videos online, contact a company such as ReputationUP, which can eliminate any harmful content.
Cyber extortion is an umbrella term that includes several cyber crimes.
Ransomware is just one of the most common ways cyber extortion can be accomplished.
Extortion refers to intimidating or threatening a person with violence for monetary compensation.
Blackmail, on the other hand, referred it is intended to threaten the person with social, emotional, or professional ruin in exchange for monetary compensation.
To prevent the consequences of cyber extortion, you need to act in advance.
Back up files on your device periodically so you don’t lose your data if it gets encrypted in an attack.
Always keep your systems and access passwords to the various services up to date.
Train your employees to avoid internal company incidents and prepare a risk management plan for any attack.
Businesses that are victims of cyber extortion suffer a data breach and the loss of sensitive information.
The consequences of such acts are damage to reputation, loss of customers and money.







