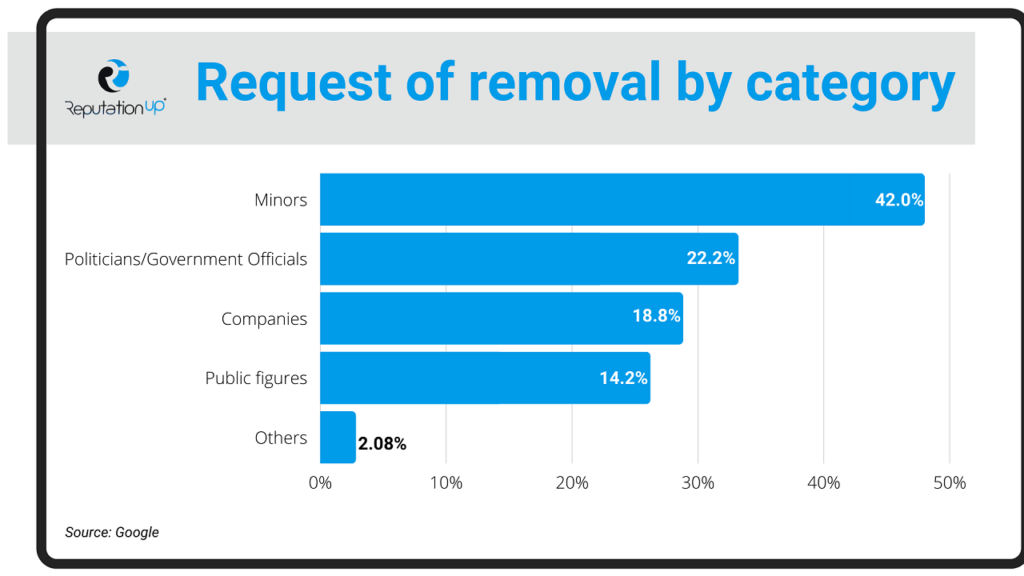
Do you want to remove no longer relevant pieces of information or outdated content? Learn what is Right to be Forgotten and how to exercise it on Google, Social Media, and Internet.
Index
Do you want to exercise your right to be forgotten?
ReputationUP eliminates any obsolete content (links, photos, videos, comments, content, reviews) and guarantees your right to be forgotten and digital privacy
What is the right to be forgotten?
The right to be forgotten is the legal protection that allows you to preserve your reputation by the storage of information that are no longer relevant, and therefore outdated for the public interest.
Within this legal framework, there is the possibility of eliminating harmful links from the web; cleaning up your online reputation; and prevent expensive crisis management operations.
The EU regulation 2016/679 has actually established that:
“The protection of natural persons in relation to the processing of personal data is a fundamental right.”
What does the Right to be Forgotten mean?
The meaning of the term Right To Be Forgotten, also called the Right to Erasure is enclosed in the etymology of the Latin term erasus, past participle of eradere, that means scrape out or Remove.
In this sense, here is also the meaning provided by the Cambridge Dictionary:
“The state of being completely forgotten.”
The right to be forgotten can therefore be defined:
The guarantee of not spreading – in the absence of particular reasons – information that can constitute a prejudicial precedent for a person’s honor.
Need help deleting embarrassing photos from the web?
ReputationUP guarantees the elimination of any photo from any platform
Birth of the Right to be Forgotten
The case of Laurence Godfrey v. Demon:
Internet Limited involves the first judicial decision within England and Wales.
Which concerns a defamatory statement made via e-mail through an Internet Usenet discussion group.
Defamation law is provided for in the Defamation Act 2013 and in the common law introducing:
“A process through which persons who believe they have been defamed,
May request the removal of information from the website operator who hosts third party content,
As well as the party who has posted the content.”
From a legislative point of view, the Right becomes concrete only many years later.

Elizabeth Denham CBE is the current UK Information Commissioner (ICO), appointed in July 2016
The Act is overseen by an Information Commissioner, who states:
“The aim of data protection legislation is to “strike a balance between the rights of individuals and the sometimes competing interests of those with legitimate reasons for using personal information.”
To fully understand the current importance of the Right to be Forgotten, it is important to remember the judgment of the European Court of Justice of 13 May 2014 (Google vs AEPD), that forced Google to erase content deemed to be harmful.
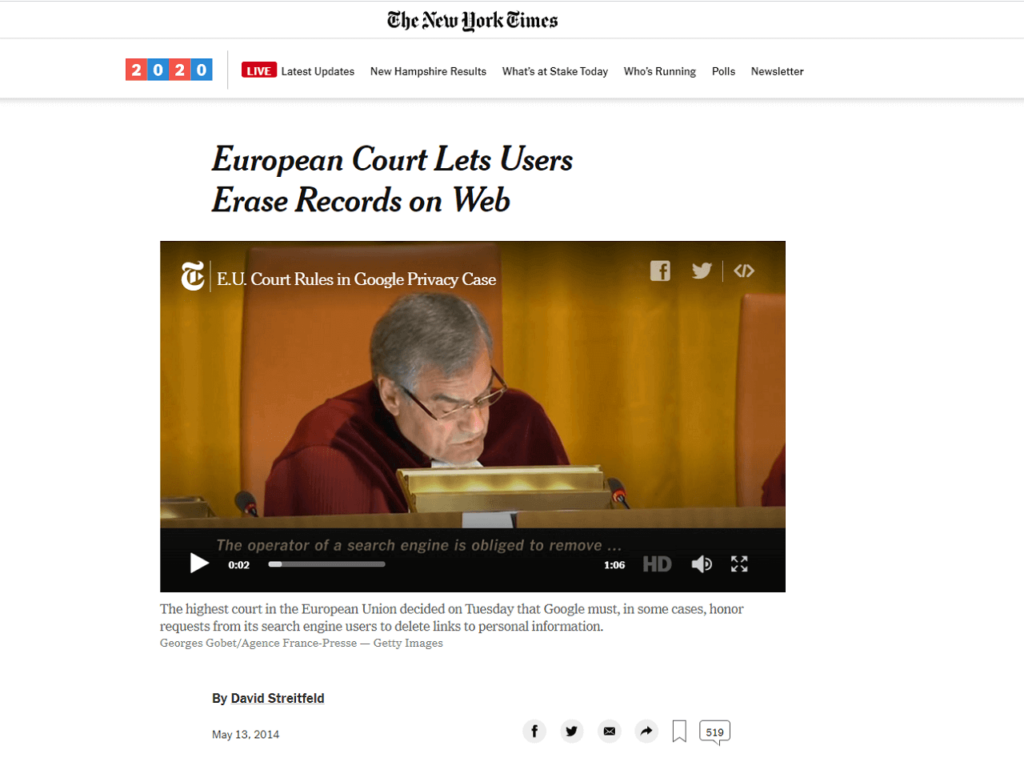
Finally, on April 27, 2016, the European Parliament launched the GDPR, which governs the matter of personal data processing, with particular reference to the right to be forgotten on the Internet, extending the protection within and outside the EU border.
Do you want to exercise your right to be forgotten?
ReputationUP eliminates any obsolete content (links, photos, videos, comments, content, reviews) and guarantees your right to be forgotten and digital privacy
What Does “Be Forgotten” Mean?
The right to be forgotten is the protection of the online reputation of the person involved in public affairs. It makes the right to privacy prevail over the right of expression, by removing information and search results from Google.
Let’s take a concrete example. If you have undergone a media trial even before a judicial trial, you risk finding yourself with a clean criminal record and a dirty online image.
When the news – harmful, defamatory and obsolete – ceases to be of public interest and falls into a private sphere, you can exercise your right, i.e. you can request that the erasure of personal data.
The ultimate goal is to improve the so-called Reputation Score, i.e. the percentage of positive net sentiment generated online by you or your brand: the higher it is, the better your reputation will be.
What does the Right to be Forgotten Provide?
In a nutshell, the Right to be Forgotten provides these fundamental points:
- Search Engine
The manager of an Internet search engine is responsible for the processing of personal data;
- Elimination
The manager is obliged to remove the links to certain web pages from the list of personal data;
- Application of the law
The law applies if the information is incorrect, inappropriate, irrelevant or excessive;
- Request for deletion
You must weigh the interests of the person involved.
A historical sentence
Noteworthy is the judgement of the European Court of Justice enacted on 13 May 2014, centered on articles 7 and 8 of the Charter of Rights.
The decision speaks for the first time of public interest as a discriminator of the freedom of expression and information when it comes to “inadequate, irrelevant or no longer relevant” information.
This allowed any EU citizen to establish a legal action for the removal of all compromising digital content that is not relevant to the public interest.

How to exercise the right to be forgotten?
Now let’s see how to exercise the right to be forgotten and ask for the erasure of content that is defamatory for your web reputation.
Here in detail the official procedure on Google and Social Networks.
Don’t like what Google says about you?
ReputationUP guarantees the elimination of any negative link (photos, videos, comments, content, reviews) from Google
How to Exercise it on Google
Self-protection is carried out by downloading directly from Google a special form to which the search engine is bound by law.
Andrea Baggio, CEO of ReputationUP, explains to us how to exercise the right to be forgotten on Google:
1) Visit the Google support guide
2) Click on “create a request”
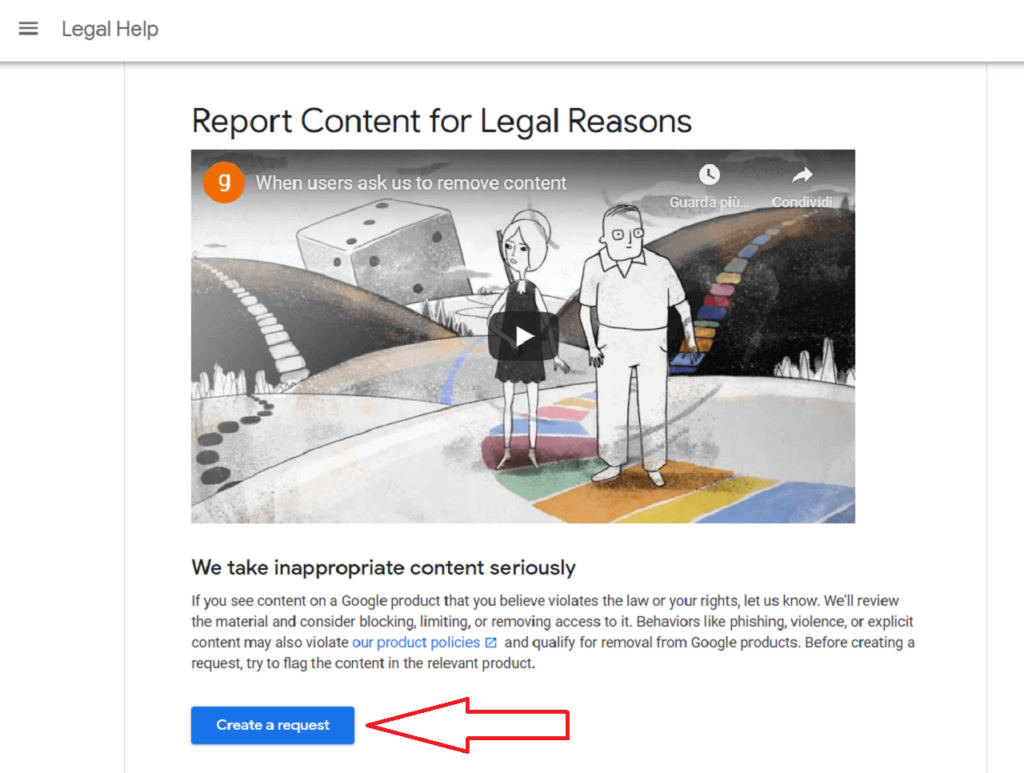
3) Enter the report page
4) Select the needed service
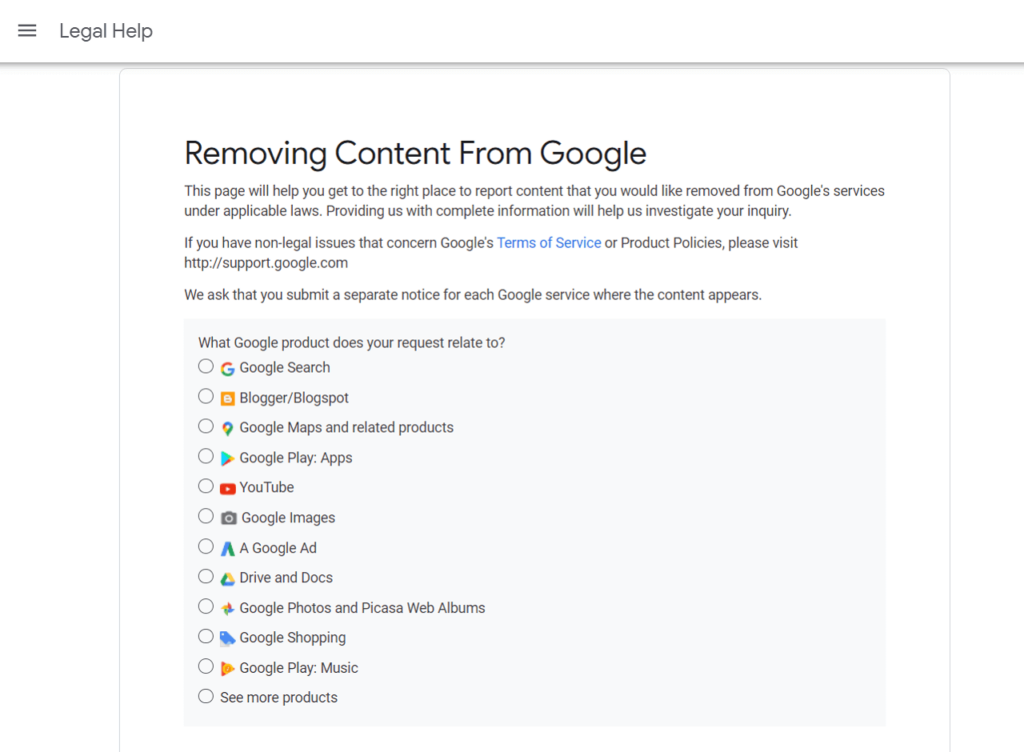
It should be noted that it can take Google a very long time, i.e. around 2 years, to take charge of your request.
The most appropriate solution – for those who need fast help – is to contact a specialized company such as ReputationUP.
Why the right to be forgotten doesn’t work
Although it is further ruled by the GDPR adopted in 2016, the right to be forgotten proves to be a mechanism that it is hard to put in practice: Google always takes too long to analyze requests for removal and de-indexing Google. And the outcomes are often negative.
Conclusions
Today, fortunately it is your right to safeguard privacy and prevent compromising content from jeopardizing your name or image.
As highlighted in the guide, the most effective and immediate solution to obtain the right to be forgotten is to contact a professional company specialized in removing negative information from the internet.
The filling of forms on Google is not enough to remove harmful URLs, in case you want immediate and secure protection.
Contact ReputationUP and avoid the spread of images, videos or news that could irreparably compromise your personal and working life.
Do you want to remove outdated news from the web?
ReputationUP guarantees the elimination of any obsolete news (links, photos, videos, comments, content, reviews) from any platform
FAQ
It is applied in order that personal and obsolete information is not disseminated on the web, when the publication does not comply with the requirements of the regulations, the right to be forgotten is made.
The main objective of this mechanism introduced by the RGPD is to protect and control the personal data of citizens, its importance is based on not violating the rights to privacy.
Cualquier persona física puede solicitar que se elimine su información personal de internet.
Yes, of course, but the waiting times for a response can take up to years.
Undoubtedly, since they are processes that are regulated by the EU regulation, in addition to that you can have much faster to exercise it.






